Ever wondered where the heart of your WordPress site resides?
It’s in the wp-config.php file. This file holds all the most important settings for your website. It stores details like your database connection information, security keys, and optional settings for debugging, performance tuning, and site configuration.
Because it controls core settings, editing wp-config.php can feel intimidating, especially for beginners. One wrong move can actually break your entire website. So, how can you safely find, open, and change this sensitive file without needing complex technical tools?
There are two main ways to access it. You can use an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client or a much simpler and safer way, which is using a specialized plugin. But before that, let’s fully understand the file.
What is the wp-config.php File?
The wp-config.php file is the most critical configuration file in your WordPress setup. It acts as a configuration map that tells WordPress how to connect to and operate your site. It’s a PHP file (a popular scripting language for the web) that contains all the essential settings WordPress needs to run.
The wp-config.php file connects your WordPress installation to your website’s database, allowing WordPress to retrieve posts, pages, and user data. If this file is missing, WordPress will display a setup wizard prompting you to enter your database details to automatically generate a new wp-config.php file.
It contains several critical pieces of information. For instance, it stores your database name, username, and password. It also holds unique security keys and salts. These are random, complex codes that help secure user passwords and cookies, making your site much harder for hackers to break into.
This file is so vital that you should never share its contents with anyone. Therefore, it’s vital to understand its key component before learning the process of modifying it.
Key Sections of wp-config.php
The wp-config.php file is written in PHP (which stands for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor), the scripting language WordPress uses. Most of the settings in this file are defined using PHP constants. A constant is essentially a fixed value that does not change while the website is running.
Here are the four key technical sections of the file and what they control:
1. MySQL Database Connection Settings
This is the most critical block of code. It acts like the login credentials that WordPress uses to connect to its data storage location (the database). If any of these values are wrong, you will see an “error establishing a database connection” message.
- DB_NAME: This constant defines the exact name of your WordPress database.
- DB_USER and DB_PASSWORD: These are the username and password that grant access to that database.
- DB_HOST: Specifies the database server’s address. On most shared hosts, it’s set to ‘localhost’, but on managed or cloud hosts (like WP Engine, Kinsta, or SiteGround Cloud), it may be a remote hostname.
- DB_CHARSET: This defines the character set (like utf8) used when creating new database tables.
⚠️ Minor note:
- DB_COLLATE often appears alongside DB_CHARSET (defaults to blank). It might be worth mentioning.
- DB_HOST is usually localhost, but on some managed hosts (e.g., Kinsta, WP Engine) it can be a remote host string — adding that nuance improves precision.
2. Authentication Keys and Salts
This section is vital for your site’s security. It consists of eight security keys and salts. These are long, random strings generated during installation or anytime later using the official WordPress Salt API.
Security keys (e.g., AUTH_KEY) add extra complexity to the data stored in user cookies. Cookies are small data files that verify a logged-in user’s identity. If you change these keys, it will automatically log out all users on your site, which is often used after a security breach.
3. Database Table Prefix
When WordPress creates tables in your database (for posts, users, etc.), it adds a short code before each table name, called a prefix. By default, this is set as: $table_prefix = ‘wp_’;.
It’s considered a best practice security measure to change this default prefix (for example, to wpxyz_). This makes it harder for automated hacking tools to guess the names of your database tables and launch attacks like SQL (Structured Query Language) injections.
4. Debugging and Advanced Settings
Near the end of the file, you find constants for developers and advanced controls.
- Debugging: The constant define( ‘WP_DEBUG’, false ); controls WordPress’s debugging mode. Setting the value to true makes WordPress show all PHP errors and warnings, which is helpful for troubleshooting.
- Memory Limit: You can increase PHP’s memory allocation by adding a line like define(‘WP_MEMORY_LIMIT’, ‘256M’); this is useful for fixing memory exhaustion errors caused by large plugins or themes.
⚠️ Important Warning: Backup Your Site Before Editing wp-config.php
Before you start looking for or editing the wp-config.php file, you need to stop and create a full backup of your WordPress site. Even a single misplaced comma or quote mark can cause a serious error and take your entire website offline.
Regardless of which method you choose to access the file—FTP client or a file manager—a backup is your safety net. If anything goes wrong during the editing process, having a recent backup ensures you can restore your website instantly.
Once you’re done with the backup, let’s begin the modification process.
2 Easy Ways To Find, Access, and Edit the Wp-config.php File
Now that you understand how vital the wp-config.php file is, let’s look at how you can actually find and edit it.
There are two main methods to do so. The file is found in the root directory of your WordPress installation. This root directory is often named public_html, www, or the name of your site.
Method 1. Use an FTP Client
The traditional and older method for file management is by using an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client. This is a separate piece of software, such as FileZilla, that you install on your computer. It allows you to connect directly to your web server to manage WordPress files.
To use this method, you first need your FTP login credentials (username, password, and hostname) from your web hosting provider. You can often find these in your FTP Accounts settings.
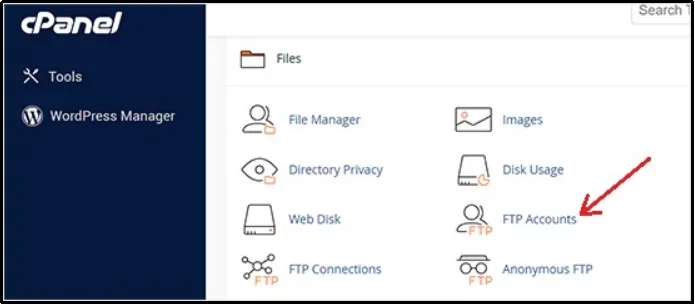
Make sure to copy the following details:
- Hostname (usually your domain or IP address),
- Username
- Password
- Port (typically port 21 for FTP or port 22 for SFTP).
If you’re unable to find these, contact your hosting support team for help.
Next, you need to establish a connection with the client that you just downloaded. We are using FileZilla. However, you can find a “Quickconnect” bar or a “Site Manager” tab that allows you to input the details you copied from your FTP client settings.
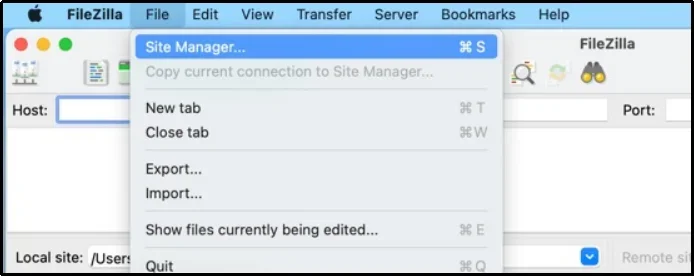
Enter the information here:
And finally, click Connect.
Once connected, navigate to the root directory to find the wp-config.php file. You must then download the file to your local computer to make your changes using a simple text editor.
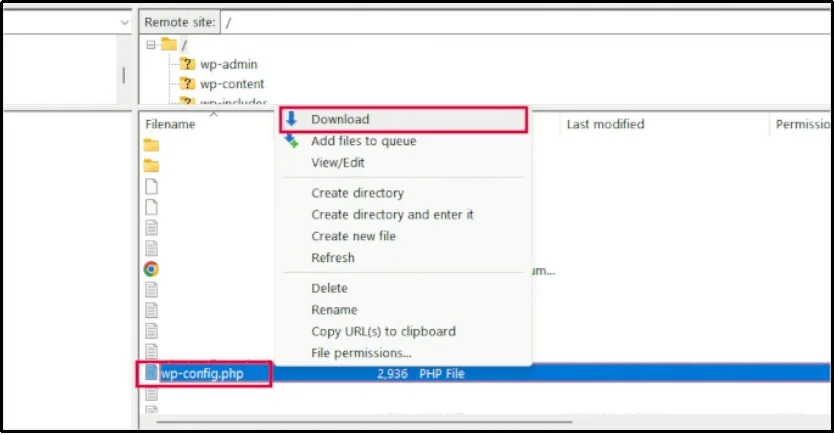
After editing, you have to upload the file back to the server and choose to overwrite the original file.
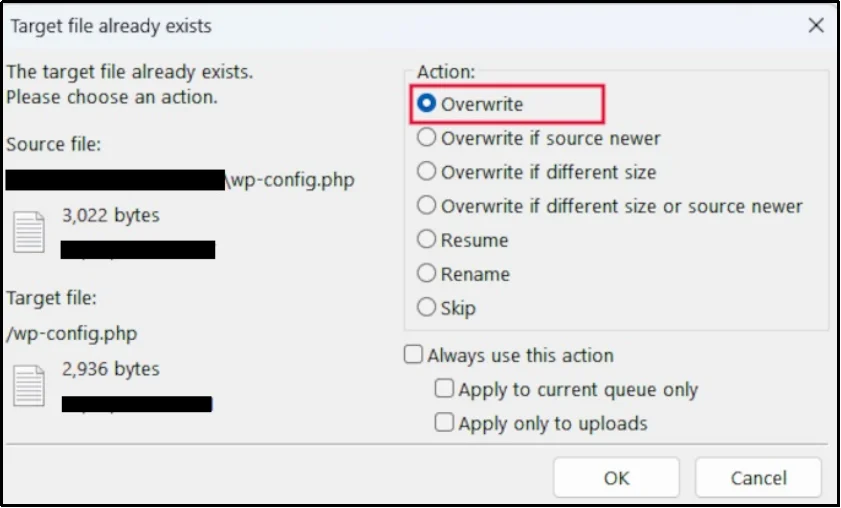
This method is time-consuming and has several risks, which is why we only recommend it for advanced users. You have to deal with extra software, remember a separate set of credentials, and constantly download and re-upload files.
More importantly, leaving your wp-config.php file on your local computer is a security risk. If your computer is compromised, a hacker could gain access to your database details. For most users, especially beginners, this process is too complicated and prone to costly errors.
Method 2. Use a WordPress File Manager Plugin
The best, safest, and most convenient way to access and modify the wp-config.php file is by using a dedicated file manager plugin. This method completely removes the need to use separate software, remember different login details, or deal with risky download/upload steps.
A file manager plugin lets you do all the work directly inside your WordPress admin dashboard.
You never have to leave your site. This is a much better approach for three key reasons:
- Safety: You edit the file on the server itself. This means your sensitive database credentials in wp-config.php are never downloaded to your personal computer, which reduces the risk of local security breaches.
- Convenience: There is no need for extra software like FileZilla or separate FTP credentials. If you can log into WordPress, you can access your files.
- Speed: You can open, edit, and save the file in just a few clicks, making the entire process much faster and simpler.
When it comes to accessing your site files with ease and maximum security, the Advanced File Manager plugin is the best choice for WordPress users. This plugin gives you a complete, professional file management system right inside your admin area. It works just like a file manager on your desktop computer.
You can use it to securely find, open, and edit any file, including the sensitive wp-config.php file, without any technical hassle.
The plugin is packed with features that make file management simple and secure:
- Complete File Operations: Copy, rename, edit, upload, download, and get complete file operations directly in the WordPress dashboard. No need for external software.
- Media & Document Previews: Instantly preview PDFs, images, audio, and video files without downloading them, saving time and improving productivity.
- Drag-and-Drop File Uploads: Upload files quickly by dragging and dropping them into the file manager interface.
- Stealth Mode for File Security: Stealth Mode hides actual file paths within the WordPress dashboard, reducing accidental exposure of sensitive directory structures.
- Advanced File Search & Sorting: Find files quickly using advanced search and sorting features, helping you manage content more efficiently.
- Keyboard Shortcuts for Speed: Speed up your tasks with straightforward keyboard shortcuts.
- Frontend File Management: Create a front-end document library that lets logged-in and (optionally) non logged-in users to access and manage shared files.
- Role-Based & User-Specific Access: Restrict file access by user role.
- Private & Public Folder Access: Set up private folders for specific users or allow public access for document sharing while maintaining security.
- Built-in Code Editor: Edit code files directly within the file manager, eliminating the need for external editors. Choose from multiple themes for a customized look. We will be using this in a while.
Now, let’s see how you can safely access and edit wp-config.php in just 4 simple steps using Advanced File Manager:
Step 1: Install and Activate Advanced File Manager
- Go to your WordPress admin dashboard and navigate to Plugins.
- Select Add Plugin.
- Search for Advanced File Manager using the search plugins feature.
- Install and activate the plugin.
Step 2: Enable PHP Code Debug Mode in the Editor
To edit the file, we will use a super-helpful plugin feature that prevents fatal errors by analyzing PHP syntax errors and won’t let you save the wp-config.php file until you fix the error.
Please note: The plugin only checks the syntax, not runtime logic.
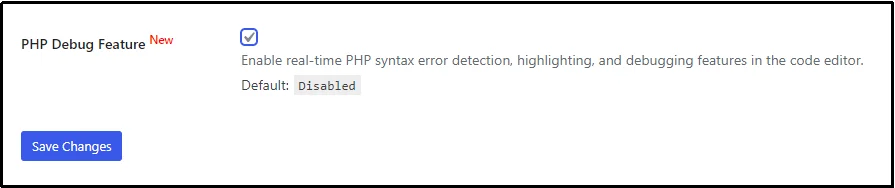
To enable this feature, navigate to the plugin’s settings and the General tab.
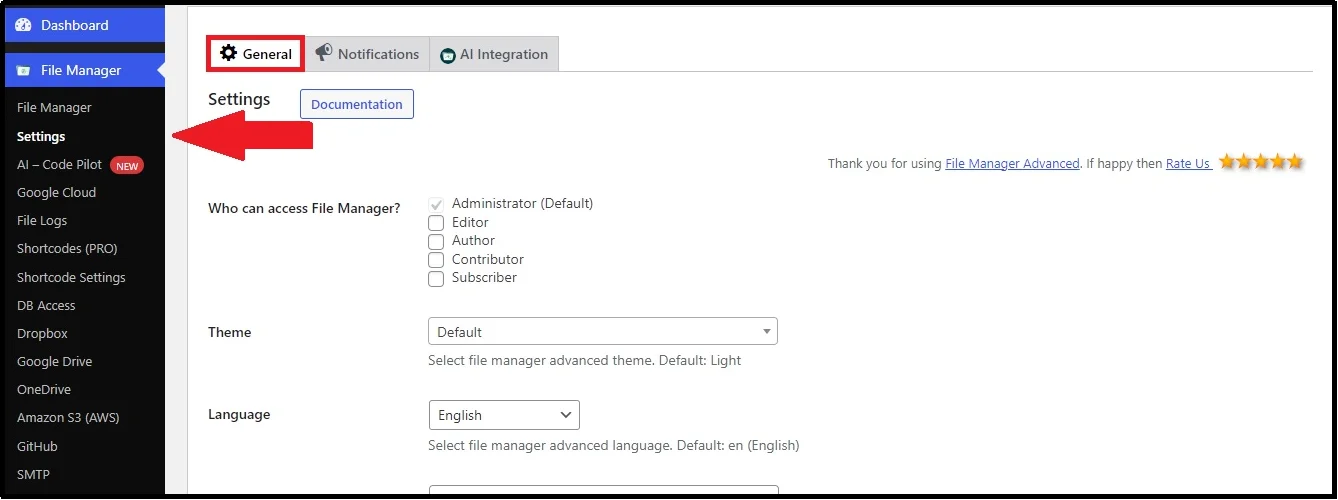
Scroll down until you find the PHP Debug Feature. Check the box and click Save Changes.
Step 3: Locate The Wp-config.php File
Now, navigate to the File Manager tab from the Admin dashboard.
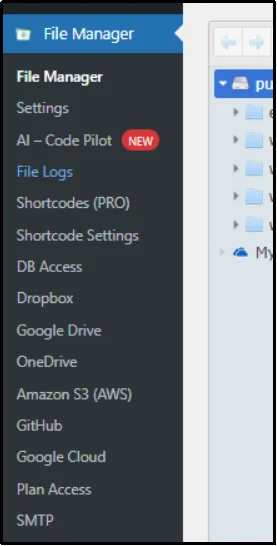
Go to the public_html folder.
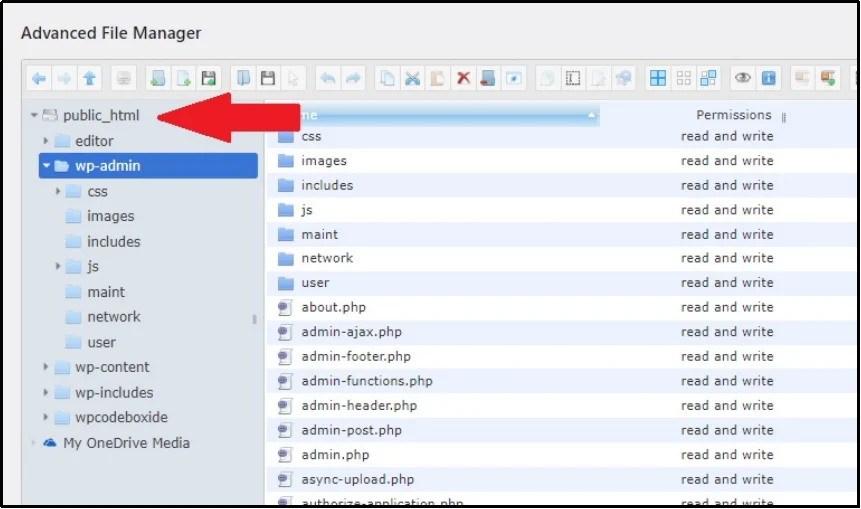
Here you can spot the wp-config.php file.
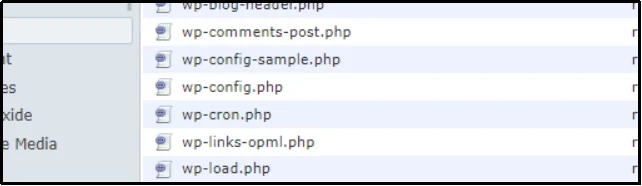
Step 4: Modify The File Using the Code Editor
💡 Security Tip: Avoid editing wp-config.php on live sites without proper access restrictions and consider restricting file access via .htaccess for added safety.
Advanced File Manager has a fantastic feature that goes hand in hand with the code editor. This feature helps prevent fatal errors and keeps your WordPress from shutting down abruptly.
Right-click on the wp-config.php file and choose Code Editor to utilize the feature.
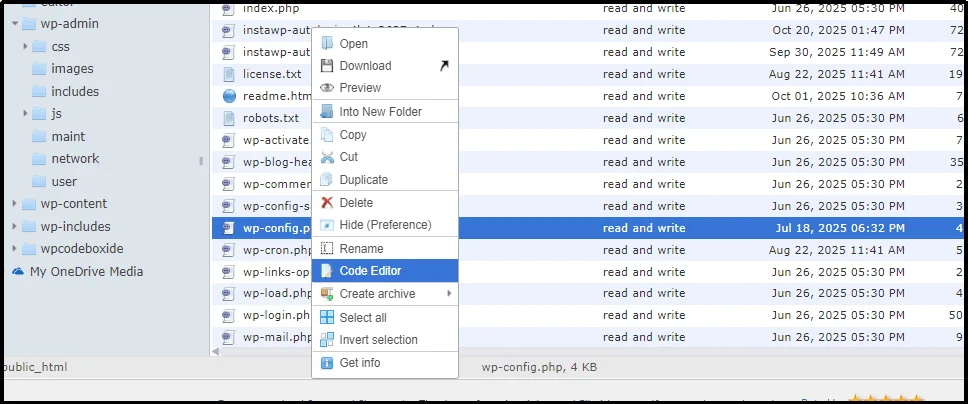
Inside, you can effortlessly edit the file and save it after making the changes. No need for any external software!
To test it, let’s save the file if it has an error. For example, if you mistakenly erase an essential comma, you will be prompted about it while saving.
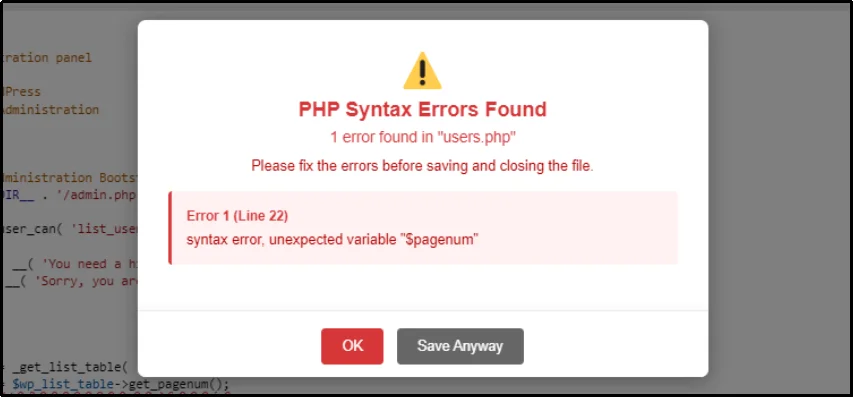
That’s how you can spot, edit, and manage wp-config.php in WordPress.
Make WordPress File Management Safer & Easier
Managing crucial files like wp-config.php doesn’t have to be a source of stress or technical complexity. By moving beyond outdated methods like FTP (File Transfer Protocol), you can adopt a faster, safer, and more efficient approach to managing your website’s most sensitive settings. The goal is to gain full control over your site’s backend without risking a fatal error.
The Advanced File Manager plugin offers the most robust solution, enabling you to edit files securely directly in your WordPress dashboard. With features like the smart Code Editor and advanced user access controls, you can perform essential maintenance tasks quickly and confidently. This control is key to keeping your WordPress site secure, optimized, and running smoothly.
Ready to unlock full security and effortless file management?
Upgrade to Advanced File Manager Premium today and safely edit wp-config.php and other crucial files directly from your WordPress dashboard!



